Thyroid disease & Diet
Nutrition plays an important role in maintaining thyroid health. Imbalance in thyroid glands impacts the body metabolism and function which causes unintended weight gain or loss and also increases the risk for heart disease and diabetes.
Thyroid gland and its functions:
The thyroid gland is a 2-inch butterfly-shaped organ located at the front of the neck. It’s small but it’s a major gland and affects nearly every organ in the body.
It’s helps to regulate:
•Fat and carbohydrate metabolism
•Respiration, body temperature
•Brain development
•Cholesterol levels, the heart and nervous system
•Blood calcium levels
•Menstrual cycles, skin integrity, and more.
Thyroid diseases & it’s signs/symptoms:
Hypothyroidism (under active hormone):
In this condition, the thyroid hormone is released in inadequate amount in the body affecting the body functions. The lack of hormone slow downs the metabolism causing
•Weight gain
•Fatigue
•Dry skin & hair loss
•Difficulty in concentrating, depression
•Joint pain
•Infertility,missed periods & miscarriage
Hyperthyroidism (over active hormone):
It’s the over secretion of thyroid hormone in the body. This causes increased body metabolism leading to following symptoms:
•Weight loss
•Increased heart beat
•High blood pressure
•Diarrhoea
•Fatigue
•Difficultly concentration
•Anxiety
•Miscarriage or infertility & missed periods.
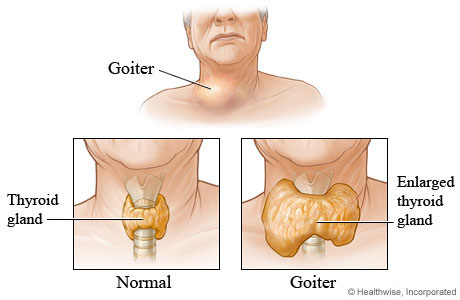
Goitre:
Goitre is the enlargement of thyroid gland which can be caused by:
•Excessive or inadequate intake of iodine in the diet
•Hypothyroidism
•Hyperthyroidism
•Thyroid cancer
Treatment:
In general not all patients require treatment. Thyroid replacement therapy is given in adequate thyroid levels to correct the imbalance. In addition to medication, surgery or oral radioactive iodine treatment may be given in hyperthyroidism depending on the disease process
Exercise:
Exercise regime helps in maintaining energy levels of the body. It is recommended to exercise in hypothyroidism to control weight gain,fatigue,and depression. In hyperthyroidism it can help regulate sleep disturbances and anxiety.
Diet in thyroid diseases:
Hyperthyroidism:
1.To avoid weight loss, add 5-6 time frequent meals and snacks in your daily diet.
2.Meals and snacks should include foods which are high in calories and proteins. This may includes milk shakes, yogurt, eggs, French toasts, meat with added fats like butter, mayonnaise, oil, cereals with added dried fruits/ honey or sugar, cream based desserts, peanuts butter and other nuts.
3.Adding at least milk,yogurt or cheese 2-3 times a day will provide calcium, phosphorous and vitamin D levels in addition to proteins.
4.Increase fluid intake 3-4L/day (until restricted by the physician)
5.Avoid caffeine containing food like coffee, tea, energy drinks which can aggravate nervousness.
6.Avoid raw natural “Goitrogens” like cabbage, Brussels, sprout, kale, cauliflower,soybeans, peanuts during anti thyroid medications. Thoroughly cooked can reduce the effect.
7.Limit large quantities of iodine Rich foods especially seaweeds.
8.A multivitamin mineral supplement may be beneficial as prescribed by the physician.
9.Avoid alcohol.
Hypothyroidism:
1.It is important to maintain weight and further gain weight.
2.Diet which is adequate in calories and carbohydrates should be taken.
3.Divide your day into 5 small meals. Add more whole grains and cereals, beans and legumes and more vegetables in your diet.
4.Fruits should be taken in between meals as snack will help increase fibre and
antioxidant.
5.Add lean meats like chicken and fish then fried or canned meats.
6.Avoid processed foods like white bread, pasta and rice, canned foods.
7.Avoid sugar.
8.Drink 2 litres of water per day.
9.Limit Natural Goitrogens in cabbage, turnips, rapeseeds,peanuts, cassava, cauliflower, broccoli, and soybeans as they may block uptake of iodine by body cells; they are inactivated by heating and cooking.
10.Use of iodised salt to achieve optimal iodine status. Avoid self iodine supplementation.
11.Multivitamin-mineral supplements may be added under supervision in case of any nutrient deficiency
Conclusion:
Healthy behaviours such as nutritious diet, exercising regularly, sleeping adequately and managing stress are essential for patients to focus during the time of treatment and afterwards.
Related Posts